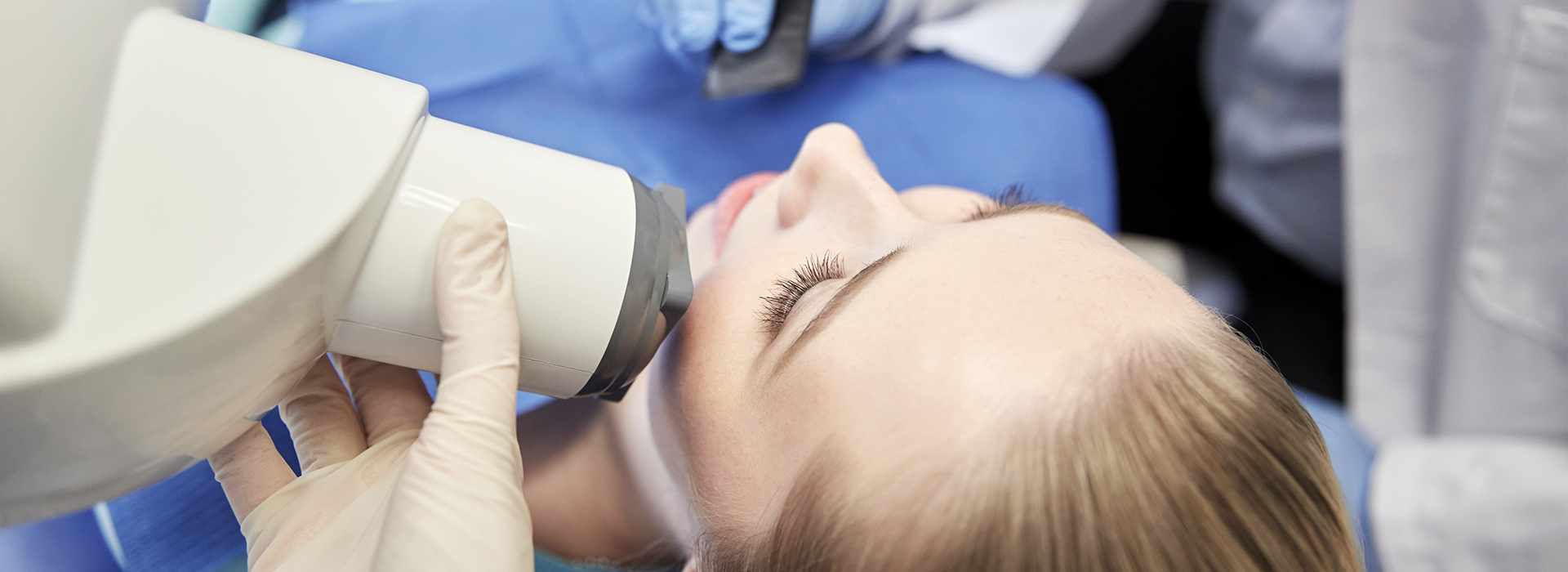
Digital radiography replaces traditional film with electronic sensors and computer processing to capture dental X-ray images. Instead of waiting for chemical development, a sensor—either intraoral or extraoral—records the radiation pattern and converts it into a digital file instantly viewable on a monitor. That digital file can be adjusted, magnified, and annotated in real time, giving clinicians a clearer view of structures that are important for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Unlike film-based systems, digital radiography uses specialized sensors that produce high-resolution images with consistent quality. The captured image becomes part of the patient’s electronic record immediately, which simplifies documentation and streamlines follow-up care. Many modern systems also include software tools that help highlight potential concerns, measure distances, and compare images over time to track changes.
Clinicians can choose between direct sensors that transmit images to a computer instantly and indirect systems that use phosphor plates that are scanned after exposure. Both approaches remove the need for film processing, improve workflow efficiency, and reduce the physical storage burden of paper radiographs. For patients, the experience is quicker and often more comfortable, with fewer procedural steps from capture to review.
One of the most important advances with digital radiography is the reduction in radiation exposure. Digital sensors are more sensitive to X-rays than film, which typically allows clinicians to use lower doses of radiation to produce diagnostically useful images. This reduction is especially valuable for routine exams and for patients who require frequent imaging, such as those undergoing complex restorative or implant planning.
Beyond lower exposure, digital imaging often shortens chair time because images appear on-screen immediately. Shorter appointments and fewer retakes contribute to a calmer, more predictable visit—an important consideration for patients with dental anxiety or medical conditions that make longer procedures difficult. Many practices also pair digital sensors with positioning aids and ergonomic designs to maximize patient comfort during imaging.
Practices that invest in digital systems typically follow established safety protocols, including proper sensor hygiene, routine equipment calibration, and adherence to recommended exposure settings. Taken together, these measures ensure that imaging is performed responsibly, with patient safety and comfort as top priorities.
Digital radiography provides clinicians with images that can be enhanced and analyzed in ways that traditional film cannot match. Contrast, brightness, and sharpness can be adjusted to reveal subtle signs of decay, bone loss, or root anatomy. Zooming and measurement tools make it easier to evaluate the exact location and size of lesions, helping clinicians plan restorative, periodontal, or endodontic treatments with greater confidence.
Because digital files are standardized and immediately accessible, they support more accurate longitudinal comparisons—an important feature when monitoring a tooth, an implant site, or progressive conditions. Software overlays and side-by-side comparisons let dentists detect even small changes over time, enabling earlier intervention when necessary and better tracking of treatment outcomes.
High-quality digital images can also reduce diagnostic ambiguity by allowing clinicians to consult with specialists quickly. When a complex case requires input from an oral surgeon, endodontist, or periodontist, a detailed digital radiograph can help the consultant understand the situation without delay, improving the coordination and precision of care.
Digital radiography is a cornerstone technology for modern, digitally driven dental practices. Because images are stored as digital files, they can be integrated with other diagnostic tools—such as intraoral scanners, 3D cone-beam CT (CBCT), and CAD/CAM systems—to create comprehensive treatment plans. These integrations enable clinicians to correlate 2D and 3D data for more precise implant placement, crown design, and surgical planning.
Digital files are easily shared with other providers or imaging centers when referrals or multi-disciplinary collaboration are required. Rather than mailing film or waiting for a physical copy, clinicians can transmit high-resolution images securely and quickly, accelerating decision-making and reducing administrative friction. This capability is especially useful for complex restorative cases, implant consultations, and second opinions.
From a practice management perspective, digital archives simplify record keeping and retrieval. Images can be indexed to patient charts, backed up securely, and retained without the space constraints of physical storage. Compliance with privacy and security standards remains essential, and reputable systems include encryption and access controls to protect patient information while allowing authorized care teams to access the images they need.
Switching from film to digital radiography has practical benefits beyond clinical performance. Digital workflows eliminate the need for chemical developers, fixer solutions, and film processing that require special handling and disposal. This reduces the practice’s environmental footprint and simplifies compliance with hazardous-waste regulations associated with chemical processing.
Operationally, digital imaging reduces turnaround time for diagnoses and streamlines communication between clinicians and patients. Clinicians can show patients their images on-screen, highlighting areas of concern with annotations and visual aids that make explanations clearer and more engaging. This visual dialogue supports informed consent and helps patients understand the rationale behind recommended treatments.
Because digital systems often integrate with practice management and imaging software, they support standardized protocols and predictable workflows. Routine maintenance, software updates, and staff training ensure the system remains reliable and continues to deliver the image quality and performance clinicians expect. Over time, these efficiencies help practices focus more on patient care and less on logistical overhead.
At Cosmetic Micro Dentistry, our investment in digital radiography reflects a commitment to accurate diagnoses, patient safety, and streamlined care. If you’d like to learn more about how digital imaging supports modern dental treatment, or how it fits into your next visit with our team, please contact us for more information.
Digital radiography is a modern imaging method that uses electronic sensors and computer software to capture and display dental x-ray images. Instead of traditional film, a small digital sensor records the image and sends it directly to a computer where it can be viewed instantly. This technology allows clinicians to adjust contrast and zoom in on areas of interest without taking additional exposures.
Images captured with digital radiography become part of the patient’s electronic record and can be reviewed alongside other diagnostic information. The immediate availability of images helps the dental team make timely, informed decisions during an appointment. Patients benefit from faster diagnoses and clearer explanations of their oral health status.
Unlike film x-rays that require chemical processing, digital radiography captures images electronically and displays them on a monitor within seconds. The digital workflow eliminates the need for development chemicals and physical storage of film, streamlining recordkeeping and reducing environmental impact. Clinicians can manipulate images digitally to enhance details that might be harder to see on film.
Because the images are stored as files, they can be copied, annotated, and compared over time with ease, which supports long-term monitoring of dental conditions. Digital images are also simpler to transmit to specialists or insurance providers when necessary. Overall, the digital approach is faster, more flexible, and more efficient for both patients and providers.
Digital radiography offers several patient-centered benefits, including quicker image capture and immediate review during the visit. The system typically requires less radiation exposure than conventional film, which enhances patient safety while still providing high-quality diagnostic images. Additionally, the ability to enlarge and enhance images helps clinicians explain findings clearly to patients.
Because images are available instantly, treatment planning and discussions can happen in a single appointment when appropriate, reducing the need for multiple visits. The elimination of film processing also means fewer environmental chemicals and faster turnaround for records requests. Overall, digital radiography improves comfort, communication, and clinical efficiency.
Digital radiography is considered safe and is widely used in modern dental practices because it typically uses lower radiation doses than traditional film x-rays. Protective measures such as lead aprons and thyroid collars are still used when appropriate to further reduce exposure. Dental professionals follow established guidelines to ensure x-rays are taken only when clinically necessary.
The sensors used for image capture are small and designed for patient comfort, and images are produced very quickly which minimizes the time a patient spends exposed. Clinicians also adhere to the principle of ALARA—as low as reasonably achievable—to balance diagnostic benefit with radiation safety. If you have specific concerns about exposure, your dental team can explain why each image is recommended and how risk is minimized.
During a digital x-ray, a small electronic sensor is positioned in the mouth near the area being examined while the x-ray unit is aimed externally at the sensor. The exposure lasts only a fraction of a second and the captured image appears almost immediately on a computer screen. The process is quick and generally well tolerated by patients of all ages.
The dental team will explain what to expect and help position the sensor for optimal imaging, and they will step behind a shield or leave the room briefly to activate the x-ray unit. Once the image is captured, the clinician can adjust brightness and contrast to highlight areas of interest and discuss findings with the patient. This immediate feedback supports accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
The frequency of dental x-rays depends on individual factors such as your oral health, age, risk of disease, and current symptoms. Patients with routine, low-risk profiles may need bitewing x-rays less frequently, while those with active disease, extensive restorations, or ongoing treatment may require more frequent imaging. Your dentist will recommend a schedule based on clinical examination and evidence-based guidelines.
For children and adolescents, x-rays are often taken more frequently to monitor development and detect early decay between teeth. For adults, x-ray intervals are personalized to monitor changes and evaluate restorative work. If you have questions about the recommended interval, discuss your history and concerns with your clinician so the imaging plan aligns with your needs.
Yes, one of the practical advantages of digital radiographs is that they can be securely shared with other providers or specialists when coordination of care is needed. Digital files can be exported, burned to a secure medium, or transmitted through encrypted platforms to ensure patient confidentiality. This capability supports collaborative treatment planning, such as when coordinating implant placement, orthodontics, or oral surgery.
When transferring images, dental offices follow privacy and security standards to protect patient information. If you are referred to a specialist, your dentist can either send images directly or provide them to you to take to the appointment. Clear communication between providers helps ensure continuity and accuracy in care.
Digital radiographs are stored in the patient’s electronic dental record using secure practice management systems and backup protocols. Access to these records is typically limited to authorized clinical staff and protected by user authentication, encryption, and routine system maintenance. Regular backups and secure servers help prevent data loss and maintain image availability for future comparison.
Practices also comply with applicable privacy regulations to safeguard patient information during storage and transmission. If you have concerns about how your images are stored or who can access them, the practice team can explain their security measures and privacy policies in detail. Transparency about recordkeeping helps patients feel confident in how their information is handled.
While digital radiography offers many advantages, it has some limitations that clinicians take into account when diagnosing and planning treatment. Certain details may be better captured with specific imaging modalities such as cone beam CT for three-dimensional assessment or extraoral radiographs for broader anatomical views. Image quality can also be affected by sensor positioning, patient movement, or improper exposure settings.
Clinicians choose the most appropriate imaging tool based on the diagnostic question at hand, sometimes combining digital intraoral images with other modalities for comprehensive evaluation. If a particular condition requires more detailed imaging, your dental team will explain the rationale and recommend the best option. The goal is to use the most informative, least invasive method to guide care.
Digital radiography enhances treatment planning by providing clear, manipulable images that improve diagnostic accuracy and communication between clinician and patient. The ability to view and annotate images in real time allows the dental team to explain findings, show expected treatment areas, and obtain informed consent more effectively. This clarity supports precise restorative work, targeted periodontal therapy, and accurate monitoring of disease progression.
At Cosmetic Micro Dentistry, we integrate digital imaging into clinical workflows to streamline diagnosis, coordinate care, and track outcomes over time. By combining digital radiographs with other technologies such as intraoral cameras and 3-D imaging when needed, the practice delivers more predictable and efficient treatment. Patients benefit from clearer explanations, fewer surprises, and better-informed decisions about their oral health.
Quick Links
Contact Us